When we walk into a bright, inviting space, lighting is often the silent hero behind that comfort. Yet behind the glow, there’s a critical question: what’s powering that brightness efficiently? As energy costs climb and sustainability becomes a shared priority, comparing LED downlights to traditional lighting isn’t just about preference—it’s about smart living and long-term savings.
Key Highlights
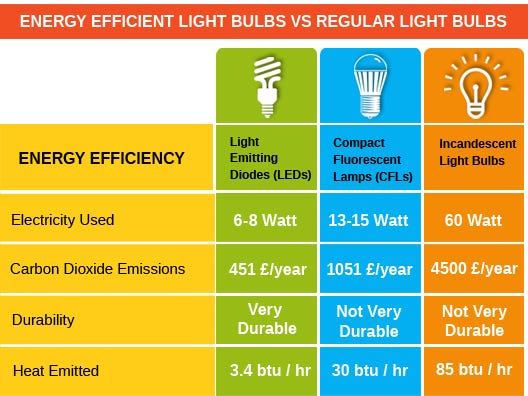
- LED downlights consume up to 80% less energy than traditional bulbs.
- They last significantly longer—often 25,000 to 50,000 hours of use.
- Lower heat output makes them safer and more efficient.
- Modern LED designs offer flexible brightness and color temperature.
- While initial costs may be higher, long-term energy and maintenance savings quickly offset them.
The Power Efficiency Difference
We’ve all seen incandescent bulbs glow warmly but burn out fast. Traditional bulbs convert most of their energy into heat rather than light—wasting up to 90% of the energy consumed. Fluorescent and halogen lamps do better but still fall short in efficiency.
LED downlights, on the other hand, convert nearly all their energy into usable light. With minimal energy wasted as heat, they illuminate more effectively while keeping electricity bills noticeably lower. In fact, replacing older fixtures with LEDs can reduce energy use by up to 75–80%, especially in frequently used areas like kitchens, offices, and hallways.
Longevity That Pays Off
Think about how often we’ve had to replace traditional bulbs. Each burnout adds up in time, cost, and hassle. LED downlights dramatically reduce that cycle.
Where a standard incandescent bulb might last 1,000 hours and a compact fluorescent around 8,000, most LED downlights last 25,000 to 50,000 hours—sometimes even more. This long lifespan means fewer replacements, lower maintenance costs, and far less waste heading to landfills.
For commercial spaces or homes with high ceilings, where replacing lights can be challenging, the longevity of LEDs offers practical peace of mind.
Heat Output and Safety
Traditional lighting generates a surprising amount of heat. Incandescent bulbs can reach temperatures over 300°F, posing risks in enclosed or insulated ceilings. Excess heat can also force HVAC systems to work harder, indirectly raising energy costs.
LED downlights emit very little heat. Their cool operation not only makes them safer but also keeps rooms comfortable. For spaces like kitchens, retail stores, or offices, this heat reduction adds another layer of energy savings and comfort.
Lighting Quality and Control
Gone are the days when LEDs meant harsh, bluish light. Modern LED downlights now offer a wide range of color temperatures—from warm, cozy tones to crisp, daylight whites. This flexibility lets us match lighting to any setting, whether it’s creating ambience in living areas or ensuring task lighting in work zones.
Many LED fixtures are also dimmable, giving us control over brightness and ambiance. That adaptability isn’t just aesthetic—it’s another way to save power. Lower brightness levels mean less energy consumption over time.
Upfront Cost vs. Long-Term Savings
It’s true—LED downlights usually cost more upfront than traditional bulbs. But the return on investment begins almost immediately. When we factor in:
- Reduced energy consumption,
- Fewer replacements,
- Lower cooling costs, and
- Minimal maintenance,
…the total savings over time make LEDs far more economical. On average, homeowners and businesses recoup their LED investment within the first couple of years through lower electricity bills alone.
Environmental Impact
Traditional bulbs contain materials like mercury (in fluorescents) and emit more carbon dioxide during energy production. LED downlights, being mercury-free and far more efficient, help reduce both environmental and health risks.
By switching to LEDs, we contribute to lowering greenhouse gas emissions and lessening landfill waste. Each LED installed brings us one step closer to sustainable, responsible energy use.
Installation and Compatibility
Another advantage of LED downlights is their versatility. They can easily fit into most existing ceiling setups, and newer models are designed for retrofit installations. Many come with integrated drivers and adjustable trims, making upgrades straightforward for both homeowners and contractors.
Plus, the slim, modern design of LED downlights complements nearly any interior—enhancing aesthetics while maximizing light coverage.
Why Energy-Smart Lighting Matters
Lighting accounts for roughly 10–15% of household energy use. That may sound small until we realize how often lights stay on throughout the day. By switching to LED downlights, we can make a tangible impact—saving energy, lowering costs, and contributing to a greener environment without compromising comfort or style.
Subtle Takeaway
Choosing LED downlights isn’t just a lighting decision—it’s an investment in comfort, efficiency, and sustainability. Whether it’s upgrading your home, office, or retail space, quality LED downlights offer the perfect balance of performance, aesthetics, and savings.
If you’re planning an upgrade, consider replacing outdated fixtures with premium LED downlights designed for longevity and brilliance. Your future energy bills—and the planet—will thank you.
FAQs
- How much energy do LED downlights really save compared to incandescent bulbs?
LED downlights use about 75–80% less energy than incandescent bulbs while providing the same brightness. - Do LED downlights work with dimmers?
Yes, many LED downlights are dimmable. However, it’s best to check compatibility with your dimmer switch to ensure smooth operation. - Are LED downlights safe for enclosed ceilings?
Absolutely. Since they emit minimal heat, LED downlights are ideal for insulated or enclosed ceiling applications. - How long do LED downlights last on average?
Most high-quality LED downlights last between 25,000 and 50,000 hours, depending on usage and quality. - Are LED downlights worth the higher upfront cost?
Yes. While they cost more initially, LED downlights quickly pay for themselves through energy savings, fewer replacements, and lower maintenance.